Imagine, while cooking, and you do not have a critical ingredients. This will stop your cooking process and cause a lot of frustration and a delay in your plans. Similarly, when such a situation arises in the manufacturing business, it results in production halting and disruptions, shipment delays, and lost sales. Businesses relying on the MRP system can overcome these challenges effortlessly. This blog post explores the following topics:
What is Material Requirements Planning (MRP)?
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a software application that manufacturers need to effectively manage their operations. It allows companies to track inventory levels to avoid overstocking, stockouts and have the needed material at the right time. MRP enables companies to schedule production activities and meet the market demands. MRP is a vital part of the manufacturing planning process to help ensure needed raw materials and sub-assemblies are available to manufacture finished goods. It helps balance supply and demand. MRP system aligns manufacturing processes with customer demand and delivery schedules, enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
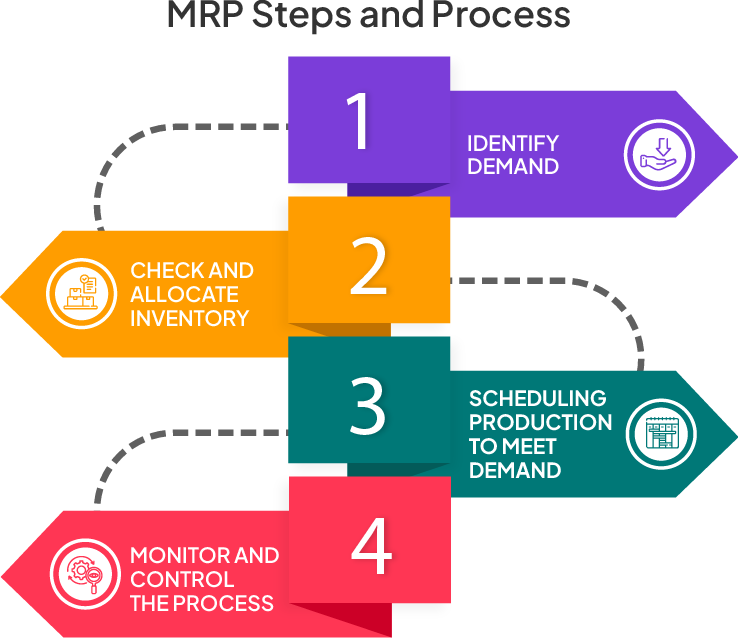
How Does MRP Work?
The key steps and MRP process that will guide how MRP works.
1. Identifying Demand
The first and foremost step of the MRP process is to identify demand. The bill of material needs to be accurate so you have visibility into the quantities of components needed to make a product. MRP then converts and displays demand into detailed requirements for raw materials and components.
2. Checking and Allocating Inventory
The second step is to check the inventory levels and where it is stored ( location). Knowing the location is essential if inventory is stored in multiple locations. Calculating inventory availability must include on-hand quantity in all appropriate locations, items in transit, and items allocated for another product.
Manufacturing companies use different production methodologies to meet demands. Some companies focusing on make-to-order utilize the MRP to check and allocate inventory based on the customer orders generated by the sales department. Some companies relying on make-to-stock generate demand forecasts to drive MRP. It helps to determine whether the inventory required to meet the demand. MRP calculates the inventory levels, recommends the materials needed to complete the order during planning, and allocates materials in the areas where they are required.
3. Scheduling Production to Meet Demands
The MRP system supplies the details to the master production schedule (MPS) system. The master production schedule links sales demand and manufacturing capacity. After identifying demand and checking inventory levels, production scheduling is done using a master production schedule. It determines the time and labor requirements to complete the production on time. It also denotes when material is needed to meet production demand. The production schedule calculates the start and end date of the production to meet on-time deliveries. It considers lead times such as material lead time (time taken to order and receive materials), production lead time (time taken to make the product and its shipment), and customer lead time (time between the customer’s order placement to delivery).
4. Monitoring and Controlling the Process
Lastly, the MRP system monitors the production process. It tracks purchase orders and monitors the production process. In case of any delays, the system notifies and sends alerts to the production and purchasing departments, allowing them to make needed adjustments.
MRP Inputs
Efficient MRP system depends on these inputs:
- Customer Orders – This is the information a company receives from a customer for a specific product order.
- Forecast Demand – This predicts the demand for a specific product based on past and present trends.
- Master Production Schedule — Customer orders and forecast demand feed the details into the master production schedule. It identifies the materials needed to make the product and schedules the production with a start and end date to meet demand on time.
- Bill of Materials (BOMs) — A bill of Materials is a product structure that determines the specific materials, subassemblies, and components in exact quantities required to make a product. It is needed for accurate planning.
- Inventory Status File (ISF) — This file shows the information and status of all raw materials, finished goods, or work-in-progress (WIP) inventory.
MRP Outputs
After the MRP receives inputs, it generates the outputs:
- Purchase Orders — These are the scheduled orders (dates) the materials is required from the supplier.
- Production Plans — These plans include details of the materials and component parts required to make finished goods, with accurate quantities and schedules.
- Inventory Reports – This includes the primary and secondary reports. It shows the quantities of materials required, performance control, deviations, and more.
MRP Vs. ERP
MRP is a component of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solution, which is a production planning tool. ERP systems include finance, accounting, HR, procurement, and customer relationship management (CRM) modules.
ERP is a solution comprising all the business management modules including MRP’s resource planning and control module providing a complete solution to manage and control an manufacturing operation.
Manufacturers using ERP systems can gain benefits such as production efficiency, time and cost savings, security, scalability, and more.
Why is Material Requirements Planning Important?
MRP gives visibility into the inventory details required to meet demand with appropriate timelines.
- Inventory Control — The MRP system is critical for effective inventory management. It helps ensure that the right material is available at the right time. It manages material availability and supply time with appropriate quantities to meet demand. It minimizes excessive inventory and prevents stockouts, optimizing inventory levels.
- Enhanced Production Efficiency — MRP reduces downtime and allocates resources, ensuring that materials are available in a required quantity when needed. It optimizes the production schedule, leading to higher productivity and production efficiency. Accurate calculations result in time and cost savings.
- Strategic Production Planning – MRP helps to continue the production operations, whether it is Just-In-Time (JIT) or Just-In-Case (JIC) production. In JIT production, MRP accurately forecast demand and ensure material availability to meet the demand on time. In JIC production, MRP helps in maintain a stock to meet unexpected demand. This results in companies carrying out operations effectively without disruptions.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction — An Effective MRP system leads to enhanced customer satisfaction. An accurate forecast and production scheduling help ensure on-time delivery, which builds reliability among customers and encourages repeated business.
The Bottom Line
MRP system is essential for efficient production management. Companies using MRP systems with a systematic process continue to grow with profitability. They can track and manage inventory levels and schedule production. Acumatica, a cloud-based ERP system, offers a powerful MRP tool for discrete and process manufacturing businesses. It facilitates manufacturers in delivering the products on time and streamlines the manufacturing process.
Contact Us
"*" indicates required fields